Main Differences Between MBR & GPT
A few points about GPT(GUID Partition Table) when compared with MBR(Master Boot Record) partitioning method for hard disk drives. GPT is the standard for laying out partitions on physical hard drives for systems running with Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) firmware. It is a standard partition layout for storage devices used in a desktop or server, such as a hard disk drive or solid-state drive. GPT has many advantages when compared with traditional MBR scheme.
Ideally, GPT is being used on servers with bigger disks volumes and MBR still remains as a favorite for home based systems such as desktops, otherwise on older server systems with disks of lesser size .
Normally parted utility would be used for larger disks which would create GPT partition scheme which otherwise performed by traditional disk utilities such as fdisk, cfdisk etc, (on Unix systems). These disk partition tools normally work for smaller disks and can only create MS-DOS partition tables, and got a few drawbacks which are overcome by parted tool.
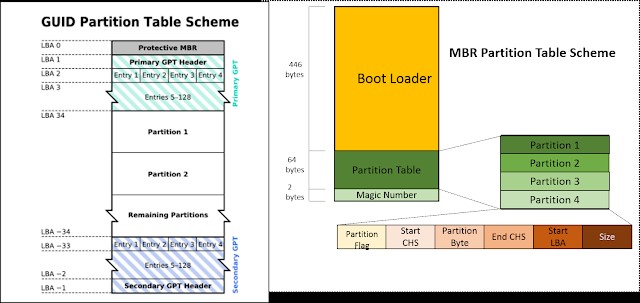
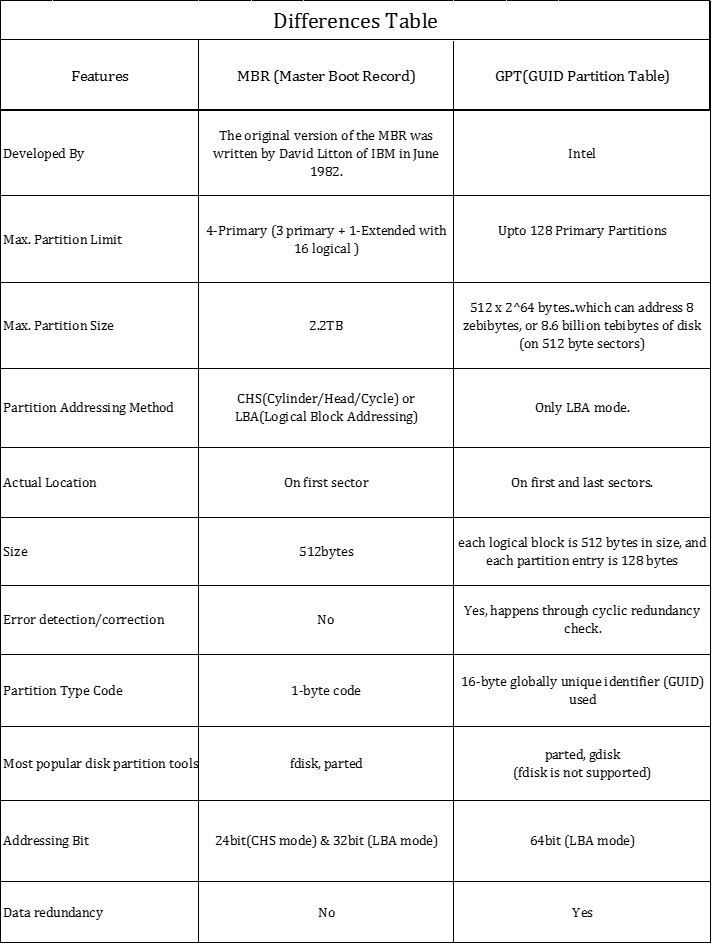
MBR & GPT considerations during installation in RHEL7.x:
Default installation program ‘anaconda’ would follow these rules while choosing partition scheme while installing GRUB2 either on MBR or GPT of the device for root file system:
- If disk is already formatted then same scheme would be retained.
If user has erased all partitions on disk or not formatted then:
If disk size is lesser or equal to 2TB then MBR scheme would be used.
If disk is larger then 2 TB then GPT partitioning scheme would be used.


